Are you eager to master Spanish conjugations and unlock the full potential of the language?
We invite you to study with us at our renowned Spanish school in Buenos Aires or our equally exceptional Spanish school in Malaga! With expert instructors, engaging lessons, and a vibrant cultural experience, we provide the perfect environment to immerse yourself in the language. Don’t miss this incredible opportunity to learn Spanish and embrace the rich heritage of these beautiful cities. Enroll now and embark on a life-changing journey with our dedicated team at your chosen destination!
Welcome to the ultimate Spanish verb conjugation guide! Are you ready to master the Spanish language and communicate confidently? With our complete Spanish verbs guide, you will have access to an extensive list of 1300 Spanish verbs and their conjugations across various tenses and moods. Ideal for both newcomers and advanced learners, this guide is designed to make learning Spanish verb conjugation easier and more efficient. Dive in, and unlock the secrets of Spanish verb conjugation mastery.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Spanish Verb Conjugation
- Also learn Por Vs Para:
- Understanding Spanish Verb Tenses
- The Importance of Regular Verbs in Spanish
- Navigating Through Irregular Verbs in Spanish
- Spanish Verb Tables: Your Go-To Conjugation Tool
- Mastering Reflexive Verbs and their Nuances
- Also Learn About Ser and Estar:
- Decoding Spanish Verb Endings for Effective Learning
- Verb Charts in Spanish: Visual Learning Aids
- Enhance Your Fluency with Spanish Verb Conjugation Practice
- Addressing Stem-changing and Orthographic Irregular Verbs
- How to Conjugate Spanish Verbs Like a Native Speaker
- Spanish Verb Conjugation Tables – A Detailed Breakdown
- Strengthening Your Mastery with Spanish Verb Forms
- Advanced Techniques for Spanish Verb Conjugation
- Top Resources for Learning Spanish Verbs More Effectively
Introduction to Spanish Verb Conjugation
Spanish verb conjugation plays an essential role in mastering the language as it enables learners to express actions and states of being across various tenses and moods by adapting verbs to suit the subject. A solid understanding of conjugation rules is integral to forming accurate sentences and communicating effectively in Spanish. This section provides an insightful introduction to the basics of Spanish verb conjugation, laying a strong foundation for more advanced learning throughout the guide.
At its core, verb conjugation in Spanish involves changing the endings of verbs to indicate the subject performing the action, the tense, and the mood being expressed. To achieve fluency in Spanish, students must familiarize themselves with three basic verb types: AR, ER, and IR verbs. Each type follows its unique conjugation pattern that students must learn and apply to specific scenarios.
Before diving into the intricacies of verb conjugation in Spanish, learners should grasp the fundamental concepts and terms prevalent in the language. They comprise:
- Infinitive: The verb’s base form, commonly ending in -ar, -er, or -ir.
- Stem: The verb’s core component that remains consistent when conjugating.
- Ending: The part of the verb that determines its tense, mood, and subject.
Consequently, mastering the structure of verb conjugation is as important as learning the individual verb endings for each tense and mood.
| Verb Type | Example Verb | Example Infinitive | Example Stem | Example Ending |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AR Verbs | Hablar (to speak) | hablar | habl- | -ar |
| ER Verbs | Comer (to eat) | comer | com- | -er |
| IR Verbs | Vivir (to live) | vivir | viv- | -ir |
Understanding the different conjugation patterns for each verb type, along with the various tenses and moods, will pave the way for effective communication in the Spanish language. This comprehensive guide offers an in-depth exploration of Spanish verbs and their conjugations, ensuring that learners acquire the necessary skills to become fluent Spanish speakers.
Also learn Por Vs Para:
Understanding Spanish Verb Tenses
Mastery of Spanish verb tenses is critical to build strong communication skills in the language. This section covers key tenses and moods, including the indicative, subjunctive, and imperative moods, to help learners effectively express themselves in Spanish.
The Indicative Mood: Present, Past, and Future Tenses
The indicative mood is used to communicate factual information and assertions. Focusing on the conjugation patterns for present, past, and future tenses, learners are equipped to discuss current events, recount past experiences, and express future intentions clearly.
- Present tense refers to actions happening at the moment or habits and facts.
- Past tense is used for completed actions or events that happened in the past. The past tense has multiple forms such as preterite (simple past) and imperfect tenses.
- Future tense expresses actions or intentions that will happen later, usually with the word “will” or “shall.”
The Subjunctive Mood: Expressing Desires and Possibilities
Spanish speakers employ the subjunctive mood to convey uncertainty, doubt, desires, emotions, and hypothetical scenarios. To enable nuanced communication, learners must learn how to use and conjugate verbs in the subjunctive mood, expressing wishes, doubts, and possibilities.
- Present subjunctive is used for expressing desires, wishes, and emotions in the present.
- Past subjunctive conveys hypothetical situations or events that didn’t occur and is often used with the conditional tense.
The Imperative Mood: Giving Commands in Spanish
The imperative mood is utilized for orders, requests, and suggestions. This section explores the rules and nuances of forming commands in Spanish, delving into different conjugations for formal and informal addresses, as well as affirmative and negative forms.
| Command Type | Formal | Informal |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | Use the third person singular or plural form of the present subjunctive. | Use the second person singular or plural form of the present subjunctive. |
| Negative | Add “no” before the third person singular or plural form of the present subjunctive. | Add “no” before the second person singular or plural form of the present subjunctive. |
Understanding these different moods and tenses in the Spanish language will enable learners to enhance their vocabulary and fluency, effectively expressing themselves in a variety of situations.
The Importance of Regular Verbs in Spanish
When learning a new language, having a strong foundation is essential for continued success in mastering its grammar and usage. In the case of Spanish, one of the most critical aspects of this foundation is understanding regular verbs and their role in the language.
Regular verbs in Spanish follow consistent conjugation patterns, which makes them predictable and easier to learn. They serve as a basis for understanding the mechanics of verb conjugation across different tenses and moods. Moreover, mastery of regular verbs simplifies the process of learning irregular verbs, as irregular verbs are primarily deviations from the standard patterns established by regular verbs.
Let’s delve deeper into the significance of Spanish regular verbs and the advantages they offer for language learners:
- Consistent conjugation rules: Regular verbs adhere to a fixed set of conjugation rules based on their endings (AR, ER, or IR). This consistency simplifies the learning process and helps students build a solid understanding of verb formation.
- Wide applicability: A large number of verbs in Spanish are regular, making them an essential component of everyday conversations and written communications. Mastering regular verbs allows learners to express themselves more effectively in various contexts.
- Easier transition to irregular verbs: As irregular verbs mainly differ from regular verbs in certain conjugation forms, having a strong grasp of regular verbs paves the way for identifying and memorizing irregular patterns with greater ease.
- Enhanced learning efficiency: By focusing initially on regular verbs, students can tackle the bulk of Spanish conjugation and sentence formation before moving on to more complex and less frequent irregular verbs.
To further illustrate the importance of regular verbs in Spanish, let’s examine a table showcasing the conjugation patterns for each verb ending:
| Verb Ending | Present Tense | Preterite Tense | Imperfect Tense |
|---|---|---|---|
| AR | -o, -as, -a, -amos, -áis, -an | -é, -aste, -ó, -amos, -asteis, -aron | -aba, -abas, -aba, -ábamos, -abais, -aban |
| ER | -o, -es, -e, -emos, -éis, -en | -í, -iste, -ió, -imos, -isteis, -ieron | -ía, -ías, -ía, -íamos, -íais, -ían |
| IR | -o, -es, -e, -imos, -ís, -en | -í, -iste, -ió, -imos, -isteis, -ieron | -ía, -ías, -ía, -íamos, -íais, -ían |
In conclusion, the importance of Spanish regular verbs cannot be overstated. As the backbone of the language’s grammar, they provide a consistent framework for verb conjugation, which ultimately streamlines the learning process and leads to increased fluency.
Navigating Through Irregular Verbs in Spanish
Irregular verbs in Spanish pose a challenge for language learners, as they deviate from standard conjugation patterns. However, with the right strategies and mnemonic devices, it is possible to remember these exceptions and navigate through them with greater ease. This section will guide you through the intricacies of irregular verb conjugation and offer helpful tips for conquering this aspect of the Spanish language.
- Ser (to be)
- Estar (to be)
- Tener (to have)
- Ir (to go)
- Decir (to say/tell)
- Hacer (to do/make)
- Poder (to be able to/can)
One essential step to learn Spanish irregular verbs is to identify the groups that share similar irregularities. These groups often exhibit similar changes in conjugation, either in stem or endings. Knowing their patterns could reduce the memorization effort for each verb.
Groups of Irregular Verbs
- Verbs with an irregular stem in the present tense
- Verbs with a stem change in the present tense
- Verbs with an irregular first-person singular conjugation
- Verbs with a stem change in the preterite tense
- Verbs with irregular conjugation in the preterite, subjunctive, and gerund forms
When learning irregular verbs, using mnemonic devices can be quite helpful. For instance, some language learners find it useful to create stories or associations linking the verb’s meaning with its irregular stem or conjugation. This technique facilitates memory retention and recall when encountering irregular verbs in context.


Additionally, practicing these verbs in context is essential for reinforcing their conjugation patterns. Ensure to incorporate them into your daily drills and conversations, focusing on various tenses and moods to become comfortable using them in real-life situations.
| Irregular Verb | Present | Preterite | Imperfect | Future | Conditional |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ser | soy, eres, es, somos, son | fui, fuiste, fue, fuimos, fueron | era, eras, era, éramos, eran | seré, serás, será, seremos, serán | sería, serías, sería, seríamos, serían |
| Estar | estoy, estás, está, estamos, están | estuve, estuviste, estuvo, estuvimos, estuvieron | estaba, estabas, estaba, estábamos, estaban | estaré, estarás, estará, estaremos, estarán | estaría, estarías, estaría, estaríamos, estarían |
| Ir | voy, vas, va, vamos, van | fui, fuiste, fue, fuimos, fueron | iba, ibas, iba, íbamos, iban | iré, irás, irá, iremos, irán | iría, irías, iría, iríamos, irían |
| Tener | tengo, tienes, tiene, tenemos, tienen | tuve, tuviste, tuvo, tuvimos, tuvieron | tenía, tenías, tenía, teníamos, tenían | tendré, tendrás, tendrá, tendremos, tendrán | tendría, tendrías, tendría, tendríamos, tendrían |
| Decir | digo, dices, dice, decimos, dicen | dije, dijiste, dijo, dijimos, dijeron | decía, decías, decía, decíamos, decían | diré, dirás, dirá, diremos, dirán | diría, dirías, diría, diríamos, dirían |
| Hacer | hago, haces, hace, hacemos, hacen | hice, hiciste, hizo, hicimos, hicieron | hacía, hacías, hacía, hacíamos, hacían | haré, harás, hará, haremos, harán | haría, harías, haría, haríamos, harían |
| Poder | puedo, puedes, puede, podemos, pueden | pude, pudiste, pudo, pudimos, pudieron | podía, podías, podía, podíamos, podían | podré, podrás, podrá, podremos, podrán | podría, podrías, podría, podríamos, podrían |
Remember, practice makes perfect. As you encounter various irregular verbs in-context or through dedicated practice, you will become more confident in using them in conversation. Just like with regular verbs, mastering irregular verbs requires consistency and repetition, so make sure to practice them regularly to solidify your grasp of the irregular verb conjugation patterns.
Spanish Verb Tables: Your Go-To Conjugation Tool
Spanish verb tables are invaluable tools for learners, providing a clear and organized visual representation of verb conjugations across all tenses and moods. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced speaker, these tables serve as quick and practical reference points to help you check and confirm correct verb forms during practice and real-life communication.
By working with Spanish verb tables, you can effectively learn and review conjugation patterns, expand your vocabulary, and build your fluency in the language. Additionally, they allow you to identify and master irregular verbs, which often deviate from standard conjugation patterns and can be particularly challenging for learners.
Some key benefits of using Spanish verb tables as your go-to conjugation tool include:
- Systematic learning and reinforcement of conjugation rules
- Quick reference points for verb forms across tenses and moods
- Opportunity to identify patterns and exceptions in verb conjugation
- Organized framework for independent study and practice
Here’s an example of a Spanish verb table for a regular AR verb “hablar” (to speak):
| Tense/Mood | yo (I) | tú (you) | él/ella/usted (he/she/you formal) | nosotros/nosotras (we) | vosotros/vosotras (you plural) | ellos/ellas/ustedes (they/you plural) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present Indicative | hablo | hablas | habla | hablamos | habláis | hablan |
| Preterite Indicative | hablé | hablaste | habló | hablamos | hablasteis | hablaron |
| Imperfect Indicative | hablaba | hablabas | hablaba | hablábamos | hablabais | hablaban |
A dedicated practice regimen with Spanish verb tables will enable you to internalize conjugation patterns and become more fluent in the Spanish language. As you progress, it becomes increasingly easier to recognize and apply the appropriate verb forms, leading to improved communication skills and greater confidence in your language abilities.
Mastering Reflexive Verbs and their Nuances
Reflexive verbs in Spanish are those that indicate the subject of a sentence performs an action upon themselves. These verbs come with their unique set of conjugation rules and pronouns. This section will elaborate on how to use reflexive verbs properly, addressing their various nuances and helping learners to incorporate them naturally into conversation.
Also Learn About Ser and Estar:
To start, reflexive verbs can be identified by the presence of se at the end of the infinitive form. For example, bañarse (to bathe oneself), peinarse (to comb oneself), and levantarse (to get up). To use these verbs, follow these steps:
- Remove the se from the infinitive form.
- Conjugate the verb according to the subject and tense.
- Add the appropriate reflexive pronoun (me, te, se, nos, os, se) before the conjugated verb.
For instance, to say “I wash myself” in Spanish:
- Remove se from lavarse (to wash oneself) – lavar.
- Conjugate lavar in the present tense for the first-person singular – lavo.
- Add the reflexive pronoun me before the conjugated verb – me lavo.
Here is a table illustrating the conjugation of the reflexive verb levantarse (to get up) in the present tense:
| Subject | Reflexive Pronoun | Conjugated Verb | Full Form |
|---|---|---|---|
| yo | me | levanto | me levanto |
| tú | te | levantas | te levantas |
| él/ella/usted | se | levanta | se levanta |
| nosotros/nosotras | nos | levantamos | nos levantamos |
| vosotros/vosotras | os | levantáis | os levantáis |
| ellos/ellas/ustedes | se | levantan | se levantan |
It’s essential to understand the nuances of Spanish reflexive verbs to use them effectively. Some verbs change their meaning when used reflexively, like dormir (to sleep) and dormirse (to fall asleep), while others can only be used reflexively, such as arrepentirse (to regret).
To master reflexive verbs in Spanish, practice conjugating and using them in different tenses and contexts, paying attention to their unique characteristics and meanings. By doing so, you will acquire a natural command over reflexive verbs and enhance your spoken and written Spanish communication skills.
Decoding Spanish Verb Endings for Effective Learning
To enhance fluency in Spanish and utilize verbs efficiently, learners must understand the conjugation rules for different verb endings. This process involves studying the conjugation patterns for AR verbs, ER verbs, and IR verbs that are the three main verb groups in the Spanish language.
AR Verbs: The Most Common Verb Type
As the most common Spanish verb type, AR verbs are essential to learn for any Spanish language student. Their conjugation patterns are relatively simple, which makes them a good starting point. Here is a breakdown of the conjugation pattern for regular AR verbs in the present tense:
| Subject Pronoun | AR Verb Ending |
|---|---|
| Yo | -o |
| Tú | -as |
| Él / Ella | -a |
| Nosotros / Nosotras | -amos |
| Vosotros / Vosotras | -áis |
| Ellos / Ellas / Ustedes | -an |
For example, the regular AR verb “hablar” (to speak) follows the above pattern: yo hablo, tú hablas, él/ella habla, nosotros/nosotras hablamos, vosotros/vosotras habláis, ellos/ellas/ustedes hablan.
ER Verbs: The Second Most Frequent Verb Type
ER verbs make up the second most frequent verb group in Spanish and have their unique conjugation patterns. The conjugation pattern for regular ER verbs in the present tense is provided below:
| Subject Pronoun | ER Verb Ending |
|---|---|
| Yo | -o |
| Tú | -es |
| Él / Ella | -e |
| Nosotros / Nosotras | -emos |
| Vosotros / Vosotras | -éis |
| Ellos / Ellas / Ustedes | -en |
Using the regular ER verb “comer” (to eat) as an example, the conjugation is: yo como, tú comes, él/ella come, nosotros/nosotras comemos, vosotros/vosotras coméis, ellos/ellas/ustedes comen.
IR Verbs: Exploring the Third Verb Group
IR verbs, as the third verb category in Spanish, also follow specific conjugation patterns. Here is the conjugation pattern for regular IR verbs in the present tense:
| Subject Pronoun | IR Verb Ending |
|---|---|
| Yo | -o |
| Tú | -es |
| Él / Ella | -e |
| Nosotros / Nosotras | -imos |
| Vosotros / Vosotras | -ís |
| Ellos / Ellas / Ustedes | -en |
For instance, in the case of the regular IR verb “vivir” (to live), the conjugation follows the pattern as: yo vivo, tú vives, él/ella vive, nosotros/nosotras vivimos, vosotros/vosotras vivís, ellos/ellas/ustedes viven.
To effectively learn Spanish verb endings, it is crucial to practice regularly. Utilize exercises that target each verb group individually before progressing to mixed groups for a well-rounded understanding of Spanish verb conjugation.
Verb Charts in Spanish: Visual Learning Aids
Verb charts serve as essential visual learning aids, helping learners of Spanish to quickly reference and review various verb conjugations. These charts present conjugation patterns for both regular and irregular verbs, across different tenses and moods. They can support a wide range of learning styles and enhance retention of conjugation patterns for new and experienced learners alike. Let’s explore some examples of helpful verb charts in Spanish and their benefits.
Regular Verb Charts
Regular verbs follow consistent conjugation patterns, and their use across the AR, ER, and IR verb endings are crucial to learn. Here is an example of a regular verb chart for the verb “hablar” (to talk) in the present tense of the indicative mood:
| Personal Pronoun | Conjugated Verb |
|---|---|
| Yo | hablo |
| Tú | hablas |
| Él/ella/usted | habla |
| Nosotros/nosotras | hablamos |
| Vosotros/vosotras | habláis |
| Ellos/ellas/ustedes | hablan |
Irregular Verb Charts
Irregular verbs deviate from standard conjugation patterns and can be more challenging for learners to master. Charts that illustrate these deviations are invaluable when practicing irregular verb forms. Here is an example of an irregular verb chart for the verb “tener” (to have) in the present tense of the indicative mood:
| Personal Pronoun | Conjugated Verb |
|---|---|
| Yo | tengo |
| Tú | tienes |
| Él/ella/usted | tiene |
| Nosotros/nosotras | tenemos |
| Vosotros/vosotras | tenéis |
| Ellos/ellas/ustedes | tienen |
Benefits of Verb Charts in Spanish
There are numerous advantages to using Spanish verb charts as visual learning aids:
- Clarity and simplicity: The clear organization of conjugation patterns in verb charts makes it easier for learners to process and understand the conjugation rules.
- Quick reference: Having a readily accessible conjugation table to review can greatly assist learners in efficiently checking verb forms while practicing or during real-life conversations.
- Memorization: Verb charts can improve memory retention by presenting conjugations visually, which can be useful for visual learners who find it easier to recall information presented in a graphic format.
- Progress tracking: By using verb charts consistently, learners can monitor their improvement and mastery of regular and irregular verb conjugations across various tenses and moods.
Using verb charts as visual learning aids can greatly enhance the proficiency and confidence of Spanish language learners. Combining these charts with regular practice exercises, exposure to native speakers, and immersive learning experiences will put you on the path to mastering Spanish verbs with greater ease.
Enhance Your Fluency with Spanish Verb Conjugation Practice
Practical application through repetitive exercises is key to achieving fluency in Spanish verb conjugation. A strategic approach that incorporates diverse practice techniques ensures optimal results. This section encourages learners to engage in routine practice, using elements like fill-in-the-blank exercises, writing prompts, and conversation drills to reinforce their knowledge and improve verb conjugation skills.
Fill-in-the-blank exercises:
Fill-in-the-blank exercises offer a simple yet effective way to test your knowledge of Spanish verb conjugations. These exercises involve completing sentences with the correct verb form, thereby allowing you to assess your understanding of various tenses and moods.
Writing prompts:
Writing prompts serve as a creative means to enhance fluency and apply your verb conjugation knowledge. Responding to prompts that require the use of specific verb tenses or moods gives you the opportunity to practice conjugation skills within a contextually relevant framework.
Conversation drills:
Engaging in conversation drills with a native Spanish speaker or a fellow learner is crucial for achieving fluency in verb conjugation. Regular practice in a conversational setting helps develop verb conjugation reflexes and increases confidence in your Spanish-speaking abilities.
Spanish Verb Conjugation Practice Ideas
- Create your fill-in-the-blank exercises or use available resources online for a personalized practice experience.
- Swap writing prompts with fellow learners, fostering peer feedback and collaborative learning.
- Join a language exchange group or use language learning platforms to participate in conversation drills with native speakers.
Recommended Verb Conjugation Practice Schedule
| Day of the Week | Activity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Fill-in-the-blank exercises | 30 minutes |
| Tuesday | Writing prompts | 30 minutes |
| Wednesday | Conversation drills | 45 minutes |
| Thursday | Fill-in-the-blank exercises | 30 minutes |
| Friday | Writing prompts | 30 minutes |
| Saturday | Conversation drills | 45 minutes |
| Sunday | Review and self-assessment | 45 minutes |
By incorporating these suggestions and maintaining a consistent practice schedule, you will significantly enhance your fluency in Spanish verb conjugation and boost your overall language skills.
Addressing Stem-changing and Orthographic Irregular Verbs
As learners progress in their Spanish language journey, they will come across two types of complex irregular verbs: stem-changing verbs and orthographic irregular verbs. It is essential to understand the alterations in their stem or spelling in various tenses and how to adjust their conjugation accordingly. In this section, we will delve into both types of irregular verbs and provide practical advice for identifying and memorizing these exceptions effectively.
Stem-changing Verbs in Spanish
Stem-changing verbs in Spanish, also known as “verbos con cambio radical,” undergo changes in their stem when conjugated in specific tenses. The vowels in the verb stem may shift according to a particular pattern, which varies depending on the verb group (AR, ER, or IR verbs) and the type of stem change (e, ie, o, and ue). The most common tenses that trigger stem changes are the present indicative, present subjunctive, and gerund.
- e → ie: These verbs change the ‘e’ in their stem to ‘ie’ when conjugated, such as pensar (to think) → pienso (I think).
- e → i: In this category, the ‘e’ in the stem changes to ‘i’ when conjugated, for example, pedir (to ask) → pido (I ask).
- o → ue: In these verbs, the ‘o’ in the stem becomes ‘ue’ when conjugated, such as dormir (to sleep) → duermo (I sleep).
Orthographic Irregular Verbs
Orthographic irregular verbs are those that exhibit spelling changes in their conjugation to maintain the pronunciation patters. These alterations generally affect the verb endings only in specific tenses and moods. The most common types of orthographic irregularities include:
- G → J: Verbs with a stem ending in ‘-ger’ or ‘-gir’ change ‘g’ to ‘j’ in certain conjugations, such as escoger (to choose) → escojo (I choose).
- Gu → G: Verbs with stems ending in ‘-guir’ drop the ‘u’ in some conjugations to keep the pronunciation consistent, for example, seguir (to follow) → sigues (you follow).
- C → Z: For verbs with a stem ending in ‘-cer’ or ‘-cir,’ the ‘c’ sometimes changes to ‘z’ when conjugated, such as conducir (to drive) → conduzco (I drive).
It is crucial to practice recognizing and conjugating stem-changing and orthographic irregular verbs in context to solidify their forms in your memory. By doing so, you will be able to use these complex conjugations effortlessly in everyday conversations, improving your overall Spanish language proficiency.
How to Conjugate Spanish Verbs Like a Native Speaker
Conjugating Spanish verbs as native speakers do requires a deep understanding of the language’s rhythm, nuances, and regional variations. This section aims to provide insights into the common practices of native speakers, including tips for mimicking their patterns and incorporating colloquial expressions into everyday speech.
To develop expertise in conjugating Spanish verbs like a native speaker, follow this guide:
- Pay attention to pronunciation: Refining your Spanish pronunciation helps in capturing the authentic rhythm of the language, making it easier to conjugate verbs naturally.
- Understand regional variations: Familiarize yourself with the most common dialects and regional differences so you can conjugate verbs appropriately according to context and location. For example, the use of “vosotros” in Spain differs from “ustedes” in Latin America.
- Mimic native speakers: Observe and imitate native speakers through conversation, audio recordings, or videos to replicate their patterns and inflections.
- Learn colloquial expressions: Incorporate informal sayings and expressions to make your speech more relatable and natural-sounding.
In addition to these tips, various resources can further support your journey to conjugate Spanish verbs like a native speaker. The table below outlines some resources, their features, and how they can help in honing your conjugation skills.
| Resource | Features | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| VerbMaster | Comprehensive verb database, illustrated lessons, progress tracking | Better understanding of conjugation patterns, enhanced vocabulary, easy monitoring of progress |
| SpanishDict | Extensive conjugation tables, video tutorials, quizzes, pronunciation guide | Improved conjugation proficiency, visual aids for learning, practice opportunities |
| Language meetups and conversation partners | Opportunities to converse with real native speakers, authentic language immersion | Real-life practice, increased fluency, better understanding of regional variations |
| Spanish movies, TV shows, and podcasts | Exposure to conversational Spanish, cultural insights, diverse range of contexts | Natural-sounding speech, grasp of colloquial expressions, appreciation of cultural nuances |
As you progress with your study of Spanish, continue practicing your conjugation skills and implementing the tips and resources mentioned above. The key to conjugating Spanish verbs like a native speaker lies in your dedication to understanding and incorporating the different aspects of the language and embracing its unique rhythm and nuances.
Spanish Verb Conjugation Tables – A Detailed Breakdown
Spanish verb conjugation tables are essential for systematic learning and reference. This section offers a detailed breakdown of these tables, explaining each tense and mood along with their corresponding verb endings. By studying these tables, learners will have a comprehensive resource to assist with the accurate formation of verb tenses. Below, we present conjugation tables for a common regular verb, “hablar” (to speak), including the indicative, subjunctive, and imperative moods, as well as the gerund and past participle forms.
| Tense/Mood | Yo | Tú | Usted/Él/Ella | Nosotros/Nosotras | Vosotros/Vosotras | Ustedes/Ellos/Ellas |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present Indicative | hablo | hablas | habla | hablamos | habláis | hablan |
| Preterite Indicative | hablé | hablaste | habló | hablamos | hablasteis | hablaron |
| Imperfect Indicative | hablaba | hablabas | hablaba | hablábamos | hablabais | hablaban |
| Conditional Indicative | hablaría | hablarías | hablaría | hablaríamos | hablaríais | hablarían |
| Present Subjunctive | hable | hables | hable | hablemos | habléis | hablen |
| Imperfect Subjunctive | hablara | hablaras | hablara | habláramos | hablarais | hablaran |
| Present Imperative | – | habla | hable | hablemos | hablad | hablen |
| Gerund | hablando | |||||
| Past Participle | hablado | |||||
These conjugation tables provide a visual aid to understanding the different tenses and moods in the Spanish language. By learning regular verbs like “hablar”, the patterns will become more familiar, making it easier to conjugate verbs in various tenses. As learners progress, they can explore more irregular verbs and fill in their own conjugation tables to help solidify their understanding of Spanish verb conjugation.
Strengthening Your Mastery with Spanish Verb Forms
To truly master Spanish verb forms, learners should go beyond memorization and seek to understand the context and application of each form. This section includes advanced exercises and techniques to help learners internalize verb forms and adapt them to various communicative situations, thus achieving a higher level of proficiency.
It’s important to realize that mastering Spanish verb forms entails more than just learning conjugation rules. One must also grasp the nuances of using these verbs in real-life contexts. Below are some useful strategies to enhance your proficiency in Spanish verb forms:
- Learn the intricacies of commonly used verbs with irregular conjugations, such as ser, ir, and hacer.
- Focus on mastering stem-changing verbs by memorizing their distinctive patterns and acknowledging their prevalence in everyday communication.
- Utilize mnemonics and memory techniques to reinforce your understanding of various verb forms and conjugations.
- Practice conjugating Spanish verbs in different tenses and moods by integrating them into real-life phrases and sentences.
- Take advantage of online platforms and language apps that provide targeted practice on formulating verb tenses and conjugations.
By employing these techniques, you’ll gradually strengthen your mastery of Spanish verb forms. To support your study routine, we’ve compiled a list of common Spanish verbs that exhibit irregularities across various tenses and offer different verb conjugation exercises, denoting the stem changes where applicable.
| Subject Pronoun | e→ie (example: empezar – to start) | o→ue (example: dormir – to sleep) | e→i (example: pedir – to ask for) |
|---|---|---|---|
| yo | empiezo | duermo | pido |
| tú | empiezas | duermes | pides |
| él/ella/usted | empieza | duerme | pide |
| nosotros/nosotras | empezamos | dormimos | pedimos |
| vosotros/vosotras | empezáis | dormís | pedís |
| ellos/ellas/ustedes | empiezan | duermen | Piden |
Practicing with exercises like these will help you better understand the conjugation patterns of various Spanish verbs, reinforcing your skills and, ultimately, improving your overall proficiency. Continued practice alongside a structured learning program will ensure you develop mastery over Spanish verb forms and elevate your ability to communicate effectively in the language.
Advanced Techniques for Spanish Verb Conjugation
Mastering Spanish conjugation requires constant practice and the right tools to succeed. Advanced techniques for Spanish verb conjugation leverage state-of-the-art technology and interactive resources to provide an engaging and adaptive learning experience. By utilizing interactive apps, immersion programs, and practical usage, learners can accelerate their journey towards Spanish conjugation mastery.


Using Technology and Apps like VerbMaster and Memrise
Modern technology and apps have taken language learning to new heights, offering innovative and effective resources for mastering Spanish verb conjugation. Two prominent apps in this domain are VerbMaster and Memrise. VerbMaster focuses on visual and interactive lessons with an extensive verb database, while Memrise provides a personalized learning journey that relies on audio features, gamification, voice recognition, and spaced repetition techniques.
| App | Features |
|---|---|
| VerbMaster |
|
| Memrise |
|
The Role of Immersion and Practical Usage in Conjugation Mastery
Immersion and practical usage are critical components of Spanish conjugation mastery. Engaging with the language through everyday conversations, listening exercises, and real-world scenarios enables learners to internalize verb forms organically. Programs like Los Cazadores de Tormentas, which employ the Conversation Based Chunking method and include audio-based stories, facilitate effective learning without the need for rote memorization.
- Listen to native speakers and engage in conversation.
- Immerse yourself in Spanish-language media (movies, TV shows, podcasts).
- Participate in social activities and events where Spanish is spoken.
- Travel to Spanish-speaking countries to experience language immersion first-hand.
In conclusion, by employing advanced Spanish verb conjugation techniques, utilizing technology apps like VerbMaster and Memrise, and practicing immersion strategies, learners can achieve Spanish conjugation mastery. As a result, they will strengthen their language skills and become confident Spanish speakers.
Top Resources for Learning Spanish Verbs More Effectively
Mastering Spanish verb conjugation is an essential part of achieving fluency in the language. To help learners on their journey, this section compiles some of the top resources for learning Spanish verbs more effectively. Utilizing these tools can significantly accelerate the learning process and enhance verb conjugation skills, making communication in Spanish much more natural and confident.
Firstly, let’s look at digital applications like VerbMaster and Memrise, which offer interactive and engaging learning experiences. VerbMaster provides illustrated lessons and a comprehensive verb database, while Memrise boasts audio features and personalized learning journeys. These apps use gamification, voice recognition, and spaced repetition to make learning Spanish verbs more enjoyable and efficient.
Another powerful method to improve Spanish verb conjugation is through immersion and practical usage. Engaging in authentic conversations, listening exercises, and real-life practice helps learners internalize verb forms more naturally than rote memorization. Language programs such as Los Cazadores de Tormentas employ Conversation Based Chunking and include audio-based stories to facilitate effective learning.
Lastly, connecting with community platforms and online resources for language learning ensures that learners receive ample support along their journey towards mastering Spanish verb conjugation. By leveraging these tools and methodologies, students can significantly enhance their understanding and application of Spanish verb forms, resulting in more effective communication and a smoother path to fluency.
As we are all aware, verbs are words that represent actions. In both English and Spanish, we conjugate verbs based on the subject performing the action. However, Spanish features a greater number of conjugations compared to English. Similar to English, verbs in Spanish can be classified as either “regular” or “irregular.” A regular verb adheres to the standard conjugation pattern, making it more predictable in form. Today, we are going to learn how to conjugate regular verbs in the present tense:
Take a look at the last two letters of each verb:
- caminar (to walk)
- leer (to read)
- abrir (to open)
Spanish has three different groups of verbs:
- -ar verbs (like caminar)
- -er verbs (like leer)
- -ir verbs (like abrir)
All three groups are infinitives. Think back to our previous lesson when we talked about infinitives. Infinitives are the original form of the verb. In English infinitives are the verbs that have the auxiliary “to” before the verb: to walk, to read, to open, etc.
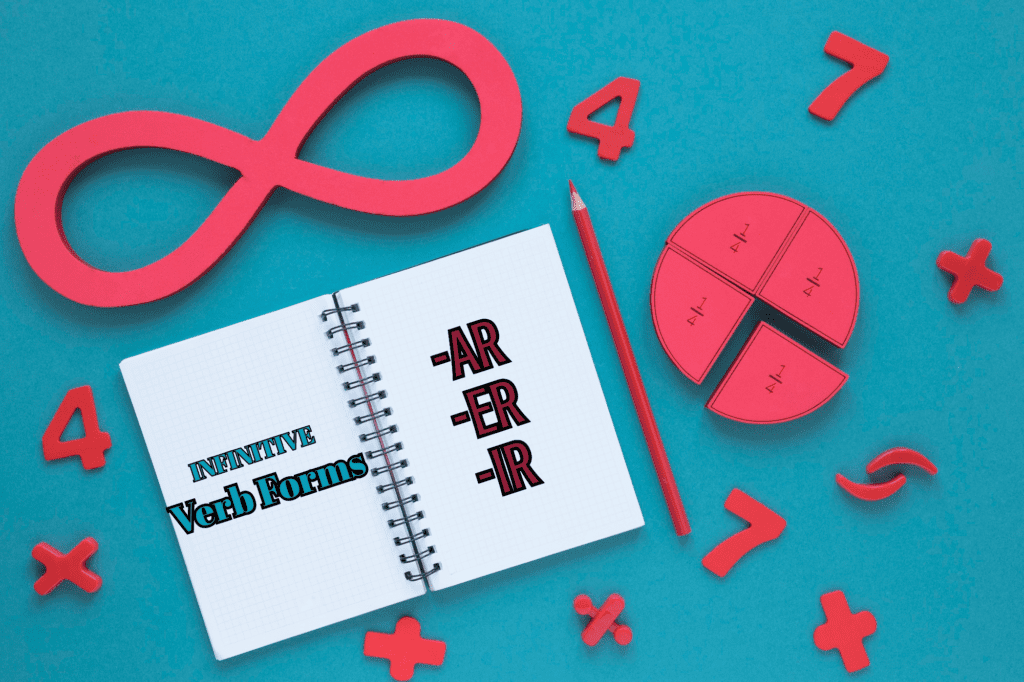

In Spanish, all infinitives end in -ar, -er, or -ir.
| -AR verb | hablar, caminar, saltar, amar |
| -ER verb | comer, leer, temer, correr |
| -IR verb | vivir, abrir, partir, vivir |
Remember what it means to conjugate a verb:
To conjugate a verb means to modify its form to reflect the tense, mood, and voice of an action, as well as to agree with the subject in terms of person (first, second, or third person) and number (singular or plural). Conjugating a verb essentially involves changing its ending to communicate who is performing the action and when the action is taking place. Please take note of the model in the chart below:
| -AR (hablar) | -ER (comer) | -IR (vivir)
----------|--------------|-------------|------------
1st sing. | hablo | como | vivo
2nd sing. | hablas | comes | vives
2nd sing. (vos) | hablás | comés | vivís
3rd sing. | habla | come | vive
1st plur. | hablamos | comemos | vivimos
2nd plur. | habláis | coméis | vivís
3rd plur. | hablan | comen | viven
*please note that the 'vos' form is used in some Spanish speaking countries such as Argentina and Ururguay instead of 'tú'. Both the 'vos' and 'tú' form are used interchangeably and have the same meaning. Now that we have introduced some regular verbs and their corresponding conjugations, let’s delve deeper into their functionality by examining their English translations:
Caminar – To walk
| Spanish | English |
| Yo camino | I walk |
| Tú caminas | You walk |
| Vos caminás | You walk |
| Él/ella camina Usted camina | He/she walks You (formal) walk |
| Nosotros/as caminamos | We walk |
| Vosotros/as caminaís | You guys walk (informal) |
| Ustedes caminan | You guys walk |
| Ellos/ellas | They walk |
Leer – To read
| Spanish | English |
| Yo leo | I read |
| Tú lees | You read |
| Vos leés | You read |
| Él/ella lee Usted lee | He/she reads You (formal) read |
| Nosotros/as leemos | We read |
| Vosotros/as leís | You guys read (informal) |
| Ustedes leen | You guys read |
| Ellos/ellas leen | They read |
Abrir – To open
| Spanish | English |
| Yo abro | I open |
| Tú abres | You open |
| Vos abrís | You open |
| Él/ella abre Usted abre | He/she opens You (formal) open |
| Nosotros/as abrimos | We open |
| Vosotros/as abrís | You guys open (informal) |
| Ustedes abren | You guys open |
| Ellos/ellas abren | They open |
Look for patterns in the various forms of the verb. Do you notice how the endings change?
In order to conjugate the I (yo) form of the verb, you drop the -ar, -er or -ir and add -o.
| Yo camino | (caminar – ar + o = camino) |
| Yo leo | (leer – er + o = leo) |
| Yo abro | (abrir – ir + o = abro) |
In order to conjugate the second person singular (tú) form of the verb, you drop the -r and add -s. When dealing with -IR verbs we drop the -ir and add -es.
| Tú caminas | (caminar – r + s = caminas) |
| Tú lees | (leer – r + s = lees) |
| Tú abres | (abrir – ir + es = abres) |
When using ‘vos’ the formula is quite similar. The only difference is that with -IR verbs we simply drop the -r and add an -s. Additionally, we add an accent mark to the last vowel.
| Vos caminás | (caminar – r + s = caminás) |
| Vos leés | (leer – r + s = leés) |
| Vos abrís | (abrir – r + s = abrís) |
In order to conjugate the he/she/you formal (él/ella/usted) form of the verb, we drop the ending and add either -a (for -ar verbs) or -e (for -er and -ir verbs).
| Él/ ella/ usted camina | (caminar – ar + a = camina) |
| Él/ ella/ usted lee | (leer – er + e = lee) |
| Él/ ella/ usted abre | (abrir – ir + e = abre) |
To conjugate the we (nosotros) form of the verb, you drop the ending and add -amos, -emos, or -imos.
| Nosotros/as caminamos | (caminar – ar + amos = caminamos) |
| Nosotros/as leemos | (leer – er + emos = leemos) |
| Nosotros/as abrimos | (abrir – ir + imos = abrimos) |
To conjugate regular -AR, -ER, and -IR verbs in the vosotros form (second person plural – informal) in the present tense, we need to remove the ending, and add “-áis” to the stem for -AR verbs, “-éis” to the stem for -ER verbs, and “-ís” to the stem for -IR verbs.
| Vosotros/as camináis | (caminar -ar + áis = camináis) |
| Vosotros/as leéis | (leer – er + éis = leéis) |
| Vosotros/as abrís | (abrir -ir + ís = abrís) |
In order to conjugate the you (ustedes) and the they (ellos/ ellas/ ustedes), you need to drop the ending and add -an ( for -ar verbs) or -en (for -er and -ir vebs).
| Ellos/ellas/ustedes caminan | (caminar – ar + an = caminan) |
| Ellos/ellas/ustedes leen | (leer – er + en = leen) |
| Ellos/ellas/ustedes abren | (abrir – ir + en = abren) |
Notice that the endings of the verbs in their infinitive forms determine the endings that their conjugated forms will take.


Maria Olson
At VAMOS Academy, I craft stories sprinkled with my love for exploration and food. Whether it’s the tang of a local dish or the rhythm of a new dialect, I bring these experiences to you. Ready for an adventure that tickles your taste buds and ignites your wanderlust? Let’s embark on this journey together, one story and one bite at a time.
Now, let’s put your skills to the test and practice conjugating regular verbs in the present tense:
FAQ
How can this guide help me master Spanish verb conjugation?
This comprehensive guide covers 1200 Spanish verbs and their conjugations in different tenses and moods, providing insights, techniques, and tools to help you practice and improve your conjugation skills. It covers various aspects of Spanish verb conjugation, such as regular and irregular verbs, reflexive verbs, and verb endings, catering to both beginners and advanced learners.
What are some important Spanish verb moods I should know about?
The indicative, subjunctive, and imperative moods are essential in Spanish verb conjugation. The indicative mood is used to express factual information, while the subjunctive mood conveys uncertainty and desires. The imperative mood is used to give orders, make requests, and offer suggestions.
Are there tools available, like verb tables or charts, to study Spanish verb conjugation more effectively?
Yes, there are various tools available to help you study Spanish verb conjugation. Verb tables and charts are particularly useful as they provide a clear and organized visual representation of verb conjugations across different tenses and moods. These tools can be used as quick reference points during practice and real-life communication.
What’s the difference between AR, ER, and IR verbs in Spanish?
In Spanish, verbs are classified into three categories based on their infinitive endings: AR, ER, and IR. Each category follows specific conjugation patterns and rules that you need to learn and practice to use them correctly in sentences.
Are there any recommended apps or online resources for practicing Spanish verb conjugation?
Some top apps and online resources for practicing Spanish verb conjugation include VerbMaster, Memrise, and Los Cazadores de Tormentas. These platforms provide interactive and adaptive learning experiences through gamification, voice recognition, and spaced repetition techniques that make learning more engaging and effective.


- Yo ________ una carta. (escribir)
- Tú ________ a la escuela. (caminar)
- Ella ________ el periódico. (leer)
- Nosotros ________ en la biblioteca. (estudiar)
- Vosotros ________ en la playa. (descansar)
- Ellos ________ una pizza grande. (comer)
- Usted ________ el informe. (revisar)
- Juan y Ana ________ música en el parque. (escuchar)
- Yo ________ mi tarea. (hacer)
- Mi hermano ________ con sus amigos. (jugar)
- Tú ________ en el concierto. (bailar)
- Nosotras ________ en la cafetería. (almorzar)
- Vosotros ________ en la reunión. (participar)
- Ustedes ________ en la tienda. (comprar)
- Ellas ________ fotografías. (tomar)
As you can see, mastering regular verb conjugations in the present tense is essential for building your Spanish fluency. By learning these conjugations, you’ll be better equipped to communicate effectively in a variety of situations. Immerse yourself in the language and embrace the rich heritage of the Spanish-speaking world as you practice and perfect your skills. Enroll in one of our language course today and take the first step towards becoming a confident Spanish speaker with the support of dedicated instructors. Your language journey awaits—don’t miss out on this incredible opportunity to grow and excel!




